What is renewable gas?

FSR Topic of the Month: Renewable Gas #2
Written by Maria Olczak and Andris Piebalgs
Biogas, biomethane, green hydrogen, and synthetic natural gas (SNG) are all forms of renewable gas. Usually, they are produced from a wide range of agricultural products and by-products such as: energy crops, livestock manure and slurry, along with various types of biowaste – sewage sludge, municipal solid waste and industrial waste (e.g. food waste)[1].
However, renewable gas can also be used to store electricity by converting it into hydrogen or methane via power-to-gas[2]. In most of the cases, renewable gas – similarly to conventional natural gas – is mostly composed of methane. While natural gas was formed over millions of years in deep underground wells, renewable gas is mostly a product of bio-chemical processes, which take up to a few days.
Biogas, biomethane and anaerobic digestion
Biogas is a result of a complex biological and chemical process known as anaerobic digestion (AD). Anaerobic means that it is oxygen-free and it consists in breaking down large organic polymers that build the organic feedstock into smaller molecules with help of chemicals and microorganisms[3].
The final products of AD are: biogas composed mainly of methane (40-70%), carbon dioxide (30-60%) and various contaminants (ammonia, water vapour, hydrogen sulphide, nitrogen, oxygen, etc.) and digestate that can be used in agriculture as natural fertilizer[4].
Biogas can be used on-site, to generate heat and electricity in a combined heat and power (CHP) plant. It can also be injected into the natural gas pipeline system and then transported to more remote customers. Yet, first it is purified and upgraded to biomethane, meaning that the content of methane is increased, so that biomethane’s quality is similar to the quality of the methane already in the gas grid. Once biomethane is injected into the grid, it blends with natural gas and has the same application[5].
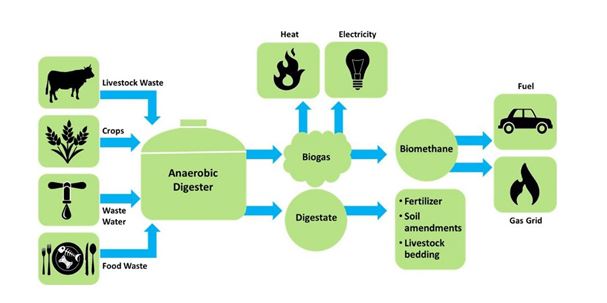
Source: Environmental and Energy Study Institute, 2017[6]
Gasification and syngas
Biomethane can be generated through other processes namely: gasification and thermochemical liquefaction processes, such as pyrolysis[7]. The gasification of biomass involves the heating of dry biomass feedstock with restricted supply of air. The product of such a process – synthesis gas (or syngas) is a mixture of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and other components such as methane. In terms of pyrolysis, biomass is heated to a high temperature ranging from 400 to 600 Celsius degrees, and without oxygen. In both cases, the gas that is a product of gasification needs to be further processed before it can be injected into the gas grid.
Power-to-Gas
Another technology that could be grouped under the renewable gas-umbrella is power-to-gas (P2G). Power-to-gas allows to convert renewable electricity into hydrogen, via electrolysis, and in the second step, to storable methane via methanation[8]. The produced synthetic natural gas (SNG) has similar properties to conventional natural gas and thus can be used as its substitute[9].
This technology is well-suited to support the use of the excess power from intermittent sources such as wind and solar, which otherwise would be curtailed, eg. due to the lack of demand. The gas network could be used to store the energy, in the form of renewable gas, and when needed, transport it to gas power plants or cogeneration plants to convert it into electricity and (or) heat. This allows for better sectoral integration between the electricity system and gas network, which was a topic of Policy Workshop organized by FSR Gas Area last fall. Moreover, both hydrogen and methane can be used as alternative fuels for mobility or as a feedstock in the chemical industry, steel plants and fuel refineries[10].
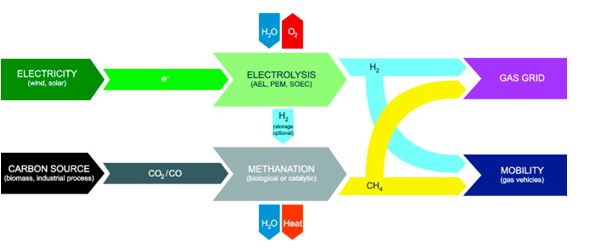
Power-to-Gas process chain
Source: Manuel Götz et al., Renewable Power-to-Gas: A technological and economic review.
‘Renewable gas’ is a semantically broad term that usually refers to biogas, biomethane, green hydrogen, and synthetic natural gas (SNG). What links different forms of renewable gas? They are relatively easy to store and are more flexible than wind or solar energy, as they can be produced in different quantities and at different periods[11]. The production of renewable gas involves the use of existing natural gas infrastructure, but at the same time is more environmentally-friendly than that of conventional gas. In short, it has most of the features of conventional natural gas, but at the same time is carbon neutral.
[1] European Biogas Association brochure: „Biogas – simply the best”, December 2011, p. 5.
[2] Renewable Gas in the Recast of the Renewable Energy Directive: A (Hidden) Opportunity?, 13 June 2017.
[3] See: <http://www.e-inst.com/biomass-to-biogas/ > (consulted on 20/02/18).
[4] S. Strauch, J. Krassowski, A. Singhal “Biomethane Guide for Decision Makers. Policy guide on biogas injection into the natural gas grid”, December 2013, p. 8.
[5] Ibid.
[6] Fact Sheet – Biogas: Converting Waste to Energy, Environmental and Energy Study Institute, 3 October 2017.
[7] Technology Roadmap. Delivering Sustainable Bioenergy. Annex 2: Bioenergy Technologies. International Energy Agency, 2017, pp. 2-3.
[8] Manuel Götz et al., Renewable Power-to-Gas: A technological and economic review, in: Renewable Energy,
Volume 85, January 2016, pp. 1371-1390.
[9] See: <http://blog.exxeta.com/energy/2017/08/22/6-facts-about-power-to-gas/> (consulted on 20/02/18).
[10] Power to Gas system solution. Opportunities, challenges and parameters on the way to marketability. German Energy Agency, November 2015, p. 4.
[11] A. Pustišek, M. Karasz, Natural Gas: A Commercial Perspective, Springer, 2017, p. 50.
FSR Topic of the Month: Renewable Gas #1
Could gas be a destination fuel for Europe?
Read the first instalment here
Don’t miss any update on this topic
Sign up for free and access the latest publications and insights















